What is the difference between AC and DC charging? | iFlowPower
Electric vehicle charging technology includes two main forms: alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC).
In the realm of electric vehicle (EV) charging, both AC (alternating current) and DC (direct current) charging methods play pivotal roles, each offering distinct advantages and catering to diverse charging needs. Let's delve deeper into the differences between these two charging methods, their underlying principles, and usage scenarios.
AC Charging:
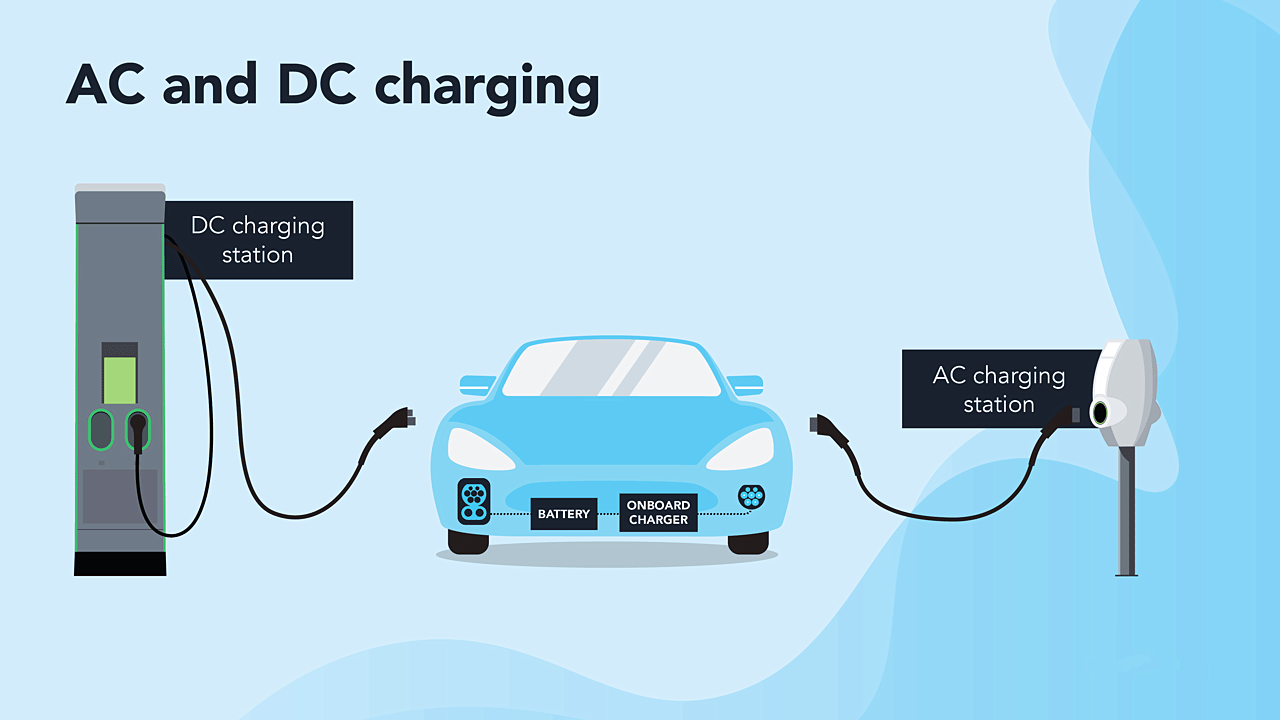
● Principle: AC charging involves converting alternating current from the power grid into the direct current needed to replenish the battery of the charging device. This conversion occurs within the vehicle through an onboard charger.
● Availability: AC charging ports are commonly found in EVs, allowing for convenient charging at home or in locations equipped with AC charging infrastructure.
● Usage Scenario: AC charging is preferred for routine charging needs, such as overnight charging at home or during extended periods of rest. Despite its slower charging speed, AC charging is cost-effective and convenient for daily use.
DC Charging:
● Principle: DC charging bypasses the need for onboard conversion by directly supplying high-voltage direct current to the vehicle's battery. The conversion from AC to DC occurs externally within the charging station.
● Availability: DC charging ports are also present in EVs, primarily used for rapid charging at public charging stations along highways and major routes.
● Usage Scenario: DC charging is favored for users requiring rapid charging solutions while on the move or for commercial charging operators seeking efficient charging services. Despite higher upfront costs, the efficiency and profitability of rapid DC charging can outweigh the initial investment.
Key Differences:
● Charging Speed: DC charging offers significantly faster charging speeds compared to AC charging, making it ideal for quick top-ups during long journeys or in high-traffic areas.
● Infrastructure: AC charging relies on onboard conversion within the vehicle, while DC charging involves external conversion equipment located within the charging station. This infrastructure difference impacts charging efficiency and speed.
● Usage Preferences: Users often choose AC or DC charging based on their specific needs and usage scenarios. AC charging is favored for routine charging at home, while DC charging is preferred for rapid charging on the go.
Conclusion:
In summary, AC and DC charging methods cater to diverse charging needs in the electric vehicle ecosystem. While AC charging is suitable for routine charging at home or during rest periods, DC charging offers rapid charging solutions for users on the move or for commercial operators seeking efficient charging services. The availability of both AC and DC charging options ensures flexibility and convenience, contributing to the widespread adoption of electric mobility.